Notebooks
Premium
Trends
BioTuring
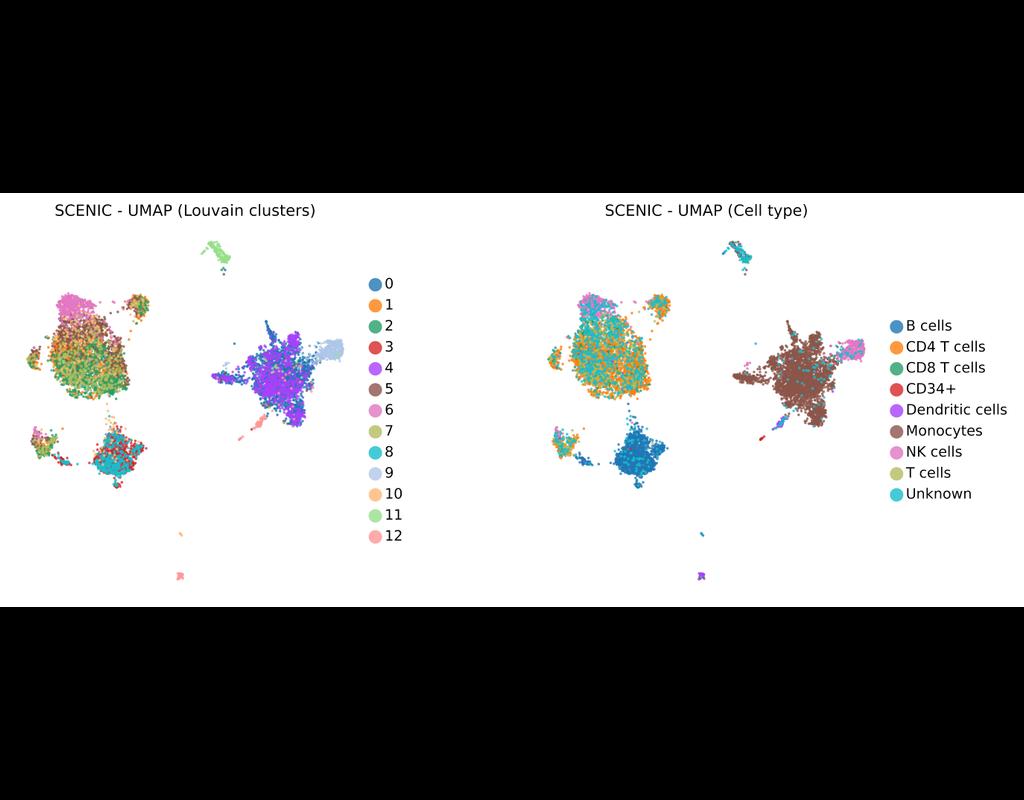
SCENIC Suite is a set of tools to study and decipher gene regulation. Its core is based on SCENIC (Single-Cell Regulatory Network Inference and Clustering) which enables you to infer transcription factors, gene regulatory networks and cell types from single-cell RNA-seq data.
pySCENIC is a lightning-fast python implementation of the SCENIC pipeline (Single-Cell Regulatory Network Inference and Clustering) which enables biologists to infer transcription factors, gene regulatory networks and cell types from single-cell RNA-seq data.